A thousand ways to represent the Earth
What are map projections of our planet and what does each one tell us?


The easiest way to represent our planet is as it is: with a globe—a sphere. But things get complicated when we need to represent it on a flat surface—a sheet of paper or a screen—to create what we know as a map. The answer to "Which is the most accurate map of the world?" or "Which world map is most similar to reality?" is confusing: all of them or none. Any cartographic projection of our planet is a simulation, a tool for a specific purpose.
Projection: from a sphere to a plane
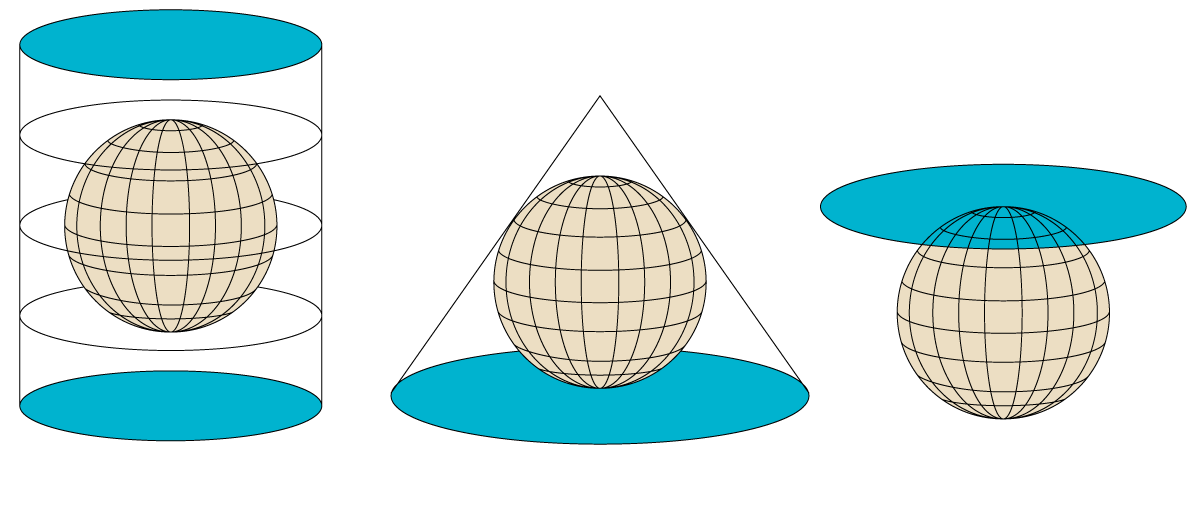
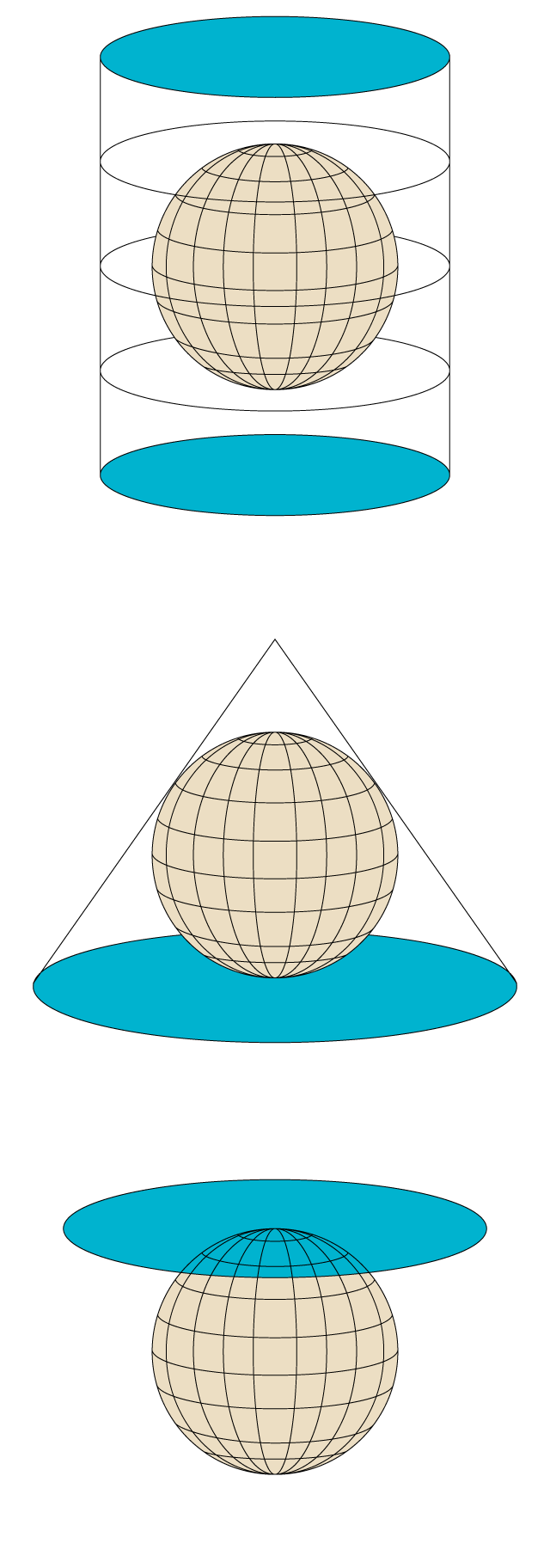
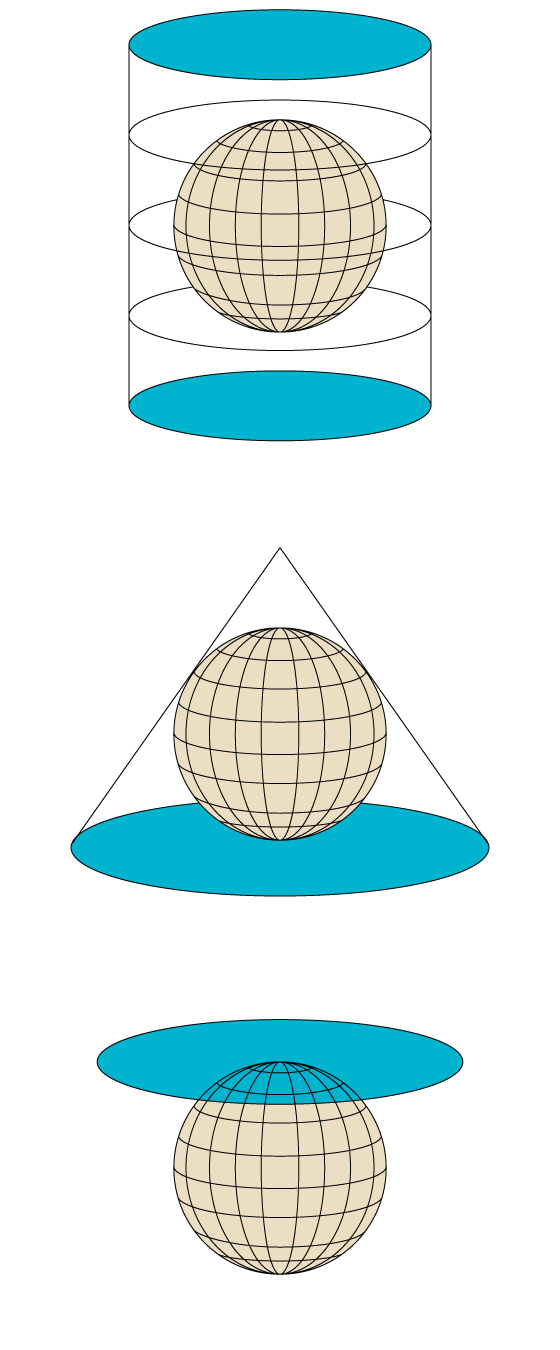
A projection is a mathematical procedure (Therefore, accurate) to represent the Earth's surface, which is spherical, on a map, which is a flat surface. According to the conceptual model, there are three main types of projections.
Because the representation of a spherical surface on a flat surface It can never be completely faithfulA projection always deforms or distorts at least one of the following properties.
- Shape: The orientation of the angles helps us to visually identify specific countries and regions. To better preserve the shape, it needs to be a local map, a smaller, more specific part within the sphere.
- Area: Relative extent or surface area of the territories represented on the map.
- Distance: The line that can be drawn between two points and that is equivalent to the same length.
- Ladder: Ratio between the distances measured on the map and those of the territories represented.
However, most maps today are made from modified projections or combinations of others to correct these distortions and obtain maps more suitable for each situation.
The right balance for the specific function
Once it is accepted that all projections are inaccurateCartographers and mathematicians have spent hundreds of years trying to find the formulas that best fulfill the purpose for which each map is created, seeking a balance between distortions. The Tissot indicatrix (red circles) shows us It helps to visualize the distortion of each mapWe observe how the Mercator projection (left) preserves shapes very well but varies the area greatly at high latitudes; in contrast, the Gall-Peters projection (right) preserves the extent of countries very faithfully but completely distorts them.
A projection is equivalent if it maintains the proportions between the areas, equidistant if it maintains distances with respect to one or more specific points and according if it maintains the shapes (angles) locally. Another type are the aphylacticWithout strictly maintaining any of the properties, they achieve a certain compromise between them.
Connected to the Mercator projection
One of the projections universally most famous It is the Mercator projection, created by the Flemish cartographer and geographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It became established as the standard projection for naval purposes thanks to its ability to represent lines in a constant true direction (that is, as if holding the direction on a compass), of vital importance at a time when... They were only guided by the directionDespite area distortions, it is generally considered a conformal projection (which preserves shapes), especially if we focus on small areas of the map.
Such a well-established projection has adapted to changing times, within certain limits, to the point that NATO used it as a basis for establishing a international coordinate systemToday, the Mercator projection is used in almost all map applications that we all consult often. However, what we do know is that it will never be as accurate as a sphere.
Other significant projections of the Earth
Robinson
Born in 1960, it was adopted by many people dissatisfied with the distortions inherent in the Mercator projection.
Dymaxion / Fuller
It is a projection of a world map onto the surface of a polyhedron that can be unfolded into a network in many different ways.
Equidistant azimuthal
Known for being the projection used in the UN logo.
Peirce quincuncial
The most distinctive property of this projection is that an infinite mosaic (like tiles) can be created.
Lambert Conformal Conic Section
Frequently used in air navigation because it is equidistant: it shows the true distance between points.
Gallo-Peters
Gall-Peters' projection attempts to escape the Eurocentric image of the world and represents the areas in an equivalent way.
Waterman
Published in 1996, this world map in the form of an unfolded truncated octahedron is also called a butterfly map for obvious reasons.
Winkel-Tripel
In 1998 the National Geographic Society adopted it as the official one to represent world maps.